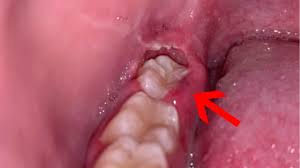
A tooth abscess is essentially a pocket filled with pus that forms due to a bacterial infection. This condition can develop in different areas of your tooth, often for various reasons. For instance, a periapical abscess occurs at the root of the tooth, while a periodontal abscess forms on the side of the tooth root, often affecting the gums. Both types are triggered by untreated issues such as dental cavities, injury, or previous dental work. If left untreated, the infection can lead to serious complications, causing swelling, inflammation, and possible damage to nearby bone and neighboring teeth.
A tooth abscess can start as a simple irritation but may grow in intensity, causing immense discomfort. As bacteria continue to invade the pulp, the innermost part of the tooth, symptoms worsen. Painful swelling, coupled with a boil or pimple, often forms on the gums, signaling an urgent need for dental attention. If ignored, the infection could spread to other areas, and in some severe cases, lead to life-threatening complications like difficulty swallowing, breathing, and even fever.
Seeking Help for a Tooth Abscess
When experiencing symptoms like painful swelling, difficulty swallowing, or breathe, it’s crucial to seek emergency medical care immediately. Left untreated, the abscess could escalate, with risks of spreading to surrounding bone and affecting neighboring teeth. Dentists often recommend draining the abscess or performing a root canal treatment to clear out the infection. In extreme cases, they may need to pull the affected tooth. Understanding and recognizing these signs will ensure timely treatment and help prevent serious health risks. Always trust your dentist and seek guidance when symptoms persist.
How a Tooth Abscess Can Affect Your Health?
An untreated tooth abscess can lead to serious complications as the infection may spread to the jawbone, soft tissues in your face and neck, and sometimes even beyond. In rare cases, the infection can travel to your heart, causing endocarditis, or to your brain, leading to bacterial meningitis. It’s crucial to address a tooth abscess as soon as possible to avoid these severe health risks. Ignoring the problem can result in life-threatening conditions that affect your overall health and well-being.
Who Is at Risk of Developing a Tooth Abscess?
- People who smoke are more likely to develop tooth abscesses.
- Dry mouth or xerostomia makes it easier for bacteria to thrive, as there is low saliva to wash them away.
- Poor oral hygiene, like not brushing or flossing regularly, increases the chances of an abscess. Regular dental cleanings are essential to keep bacteria in check.
- If you have a weakened immune system, whether due to diseases or medications, your immune response may not be strong enough to fight off germs, making you more susceptible to infections like a tooth abscess.
Symptoms and Causes
Severe Toothache
A tooth abscess often causes a severe, constant, and throbbing toothache. The pain may be described as gnawing, sharp, or shooting and can spread to the jaw, neck, or ear, making it difficult to function. If the pain is continuous, it could indicate that the infection has become more severe, causing irritation in the affected areas of the jaw.
Sensitivity to Temperature and Pressure
When you experience pain or discomfort with hot or cold temperatures, or pressure while chewing or biting, it’s a clear sign of an abscess. The gum around the affected tooth might show redness or swelling due to irritation, making it sensitive to any kind of pressure applied to it.
Swelling and Difficulty Swallowing or Breathing
An abscess can lead to swelling in your face, neck, or cheeks, and in severe cases, it may cause difficulty swallowing or breathing. If you notice these symptoms, it’s critical to seek emergency care. The swelling can also affect the lymph nodes, which may become swollen and tender, indicating the immune system is fighting off the infection.
Swollen Lymph Nodes
The lymph nodes near your jaw or neck may become swollen and tender when dealing with an abscessed tooth. These symptoms suggest that the immune system is in overdrive and trying to fight off the infection caused by bacteria. If the lymph nodes are painful, it’s important to visit a dentist as soon as possible.
Foul Odor or Taste
A common sign of a ruptured abscess is the presence of a foul-smelling or bad-tasting fluid in your mouth. This may feel like a rush of salty or bad-tasting fluid, offering temporary pain relief. The pus in the abscess can give off a bad-smelling odor, which is often accompanied by a foul taste in your mouth, signaling that the infection is not only affecting your tooth but also your overall oral health.
What Causes a Tooth Abscess?
- Bacteria can invade the dental pulp, which is the innermost part of the tooth. This infection can lead to a tooth abscess as the bacteria spread through the root, causing swelling and inflammation at the tip of the root.
- Dental cavities, often caused by tooth decay, are one of the primary causes of an abscessed tooth. Bacteria break down sugars from food and drink, creating acid that damages the enamel, and can result in severe cavities.
- A cracked or chipped tooth can allow bacteria to seep into the pulp, increasing the risk of an abscess. Even old, worn-out dental work can create small openings for bacteria to enter.
- Periodontal disease can cause an infection in the gum tissues and spread to the surrounding tissues of the teeth, resulting in an abscess. If not treated, gum disease can progress, allowing bacteria to access deeper tissues.
- Trauma to the tooth can also cause an abscess. If an injury causes damage to the tooth’s pulp, it can make the tooth more susceptible to infection and result in an abscess, sometimes even years after the trauma.
Diagnosis & test
How Is a Tooth Abscess Diagnosed?
- Your dentist will tap on your teeth to check for sensitivity to touch or pressure, which can help identify if you have an abscess.
- A dental X-ray is commonly recommended to identify the abscess and see if the infection has spread to other areas.
- If the infection has reached the neck or other areas, a CT scan may be suggested to assess the extent of the infection.
- Thermal tests may also be conducted to determine the health of your tooth pulp and how sensitive the tooth is to temperature changes.
- Your dentist will also review any history of trauma to your tooth and analyze images or previous X-rays to help with an accurate diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment options.
Treatment Options for a Tooth Abscess
- Incision and drainage: The dentist may incise the abscess and make a small cut to drain the pus. After the pus is drained, the area is typically washed with salt water (saline) to prevent further infection.
- Root canal: If the infection has affected the tooth pulp, the dentist may recommend a root canal. This procedure removes the infected pulp, drains the abscess, fills the space with a material, and seals it to prevent future infections. The tooth may be capped with a crown to make it stronger.
- Tooth extraction: If the tooth cannot be saved, the dentist may recommend pulling the affected tooth to eliminate the infection. This is done when the tooth is damaged beyond repair.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed to fight the infection. These may be used if the infection has spread to nearby teeth, the jaw, or other areas. Antibiotics can help reduce the spread of bacteria.
- Restored care: After treatment, it’s important to care for the restored tooth properly, especially if a root canal or crown is used. With good care, the tooth can last a lifetime.
How to Prevent a Tooth Abscess
- Reduce the risk of developing a tooth abscess by visiting your dentist routinely for dental check-ups and cleanings.
- Avoiding tooth decay is essential for preventing a tooth abscess. Always brush your teeth for two minutes twice a day using fluoride toothpaste to protect against decay.
- Floss your teeth daily or use a water flosser to clean between your teeth and maintain oral hygiene.
- Drink water with fluoride to strengthen your teeth and help prevent cavities. If your tooth becomes loose or chipped, make an appointment with your dentist right away.
- Eat healthy food, limiting sugary items and between-meal snacks that can contribute to tooth decay.
- Replace your toothbrush every 3 to 4 months or when the bristles become frayed to ensure effective cleaning.
- If you feel tooth pain, it’s a sign you should see your dentist. While waiting for your appointment, warm saltwater rinses can help reduce discomfort, and over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen, naproxen, or ibuprofen can ease the pain.
- There is no home remedy that can permanently solve a tooth abscess; visiting the dentist is the only way to properly treat it.
What to Expect for Your Tooth Abscess Prognosis
If you experience mouth pain, toothache, or notice a red, swollen bump on your gums, it is important to schedule an appointment with your dentist. Delaying treatment could cause the infection to spread to other areas of your tooth, leading to more severe issues.
When Is It Time to Visit the Emergency Room?
If you have a tooth abscess and develop a fever over 100.4°F (38°C), or experience difficulty swallowing, facial swelling, confusion, or an elevated heart rate, it’s critical to head to the emergency room immediately. These symptoms may indicate that the infection is spreading rapidly.
Key Questions to Ask Your Dentist About an Abscess
When visiting your dentist, ask about the abscessed tooth, its symptoms, and what tests need to be run. You should also inquire about the best course of action for your condition and whether there are any alternative treatment plans available to address the infection.